What Are Hemorrhoids (Piles)?
Hemorrhoidal tissue is a normal part of human anatomy, located within the anal canal and perianal area, consisting of blood vessels, connective tissue, and a small amount of muscle. In a minority of people, hemorrhoids can become enlarged and symptomatic.
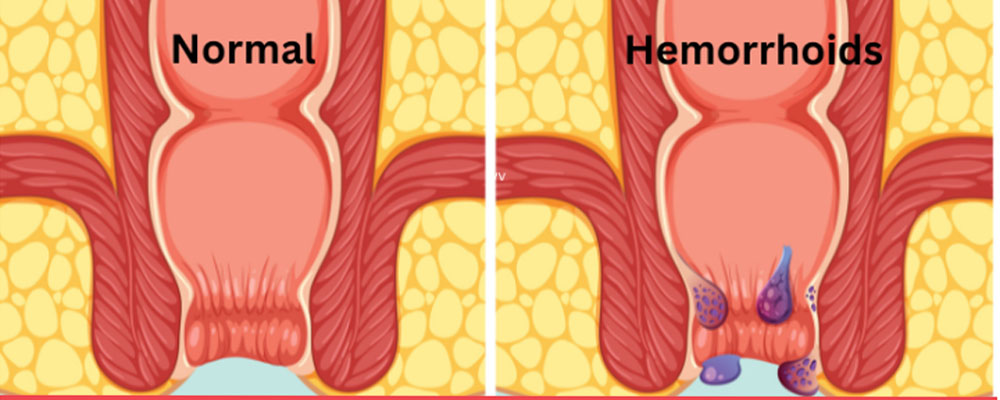
Types of Hemorrhoids
There are two main types of hemorrhoids: internal and external.
Internal Hemorrhoids: These are covered with a lining called mucosa, which is not sensitive to touch, pain, stretch, or temperature.
External Hemorrhoids: These are covered by skin that is very sensitive to touch, pain, stretch, and temperature.
Symptoms
Approximately 5% of people develop symptoms related to their hemorrhoids, and only a small fraction of these patients require surgical treatment. Symptoms can arise from internal, external, or both types of hemorrhoids.
Internal Hemorrhoids
Common symptoms of internal hemorrhoids include painless rectal bleeding or prolapse of anal tissue. Prolapse refers to hemorrhoidal tissue coming from inside the anus, which can be felt outside during wiping or bowel movements. This tissue may retract on its own or be pushed back inside by the patient. Symptoms progress slowly and intermittently.
Internal hemorrhoids are classified by their degree of prolapse:
- Grade One: No prolapse
- Grade Two: Prolapse that retracts on its own
- Grade Three: Prolapse that must be pushed back in by the patient
- Grade Four: Prolapse that cannot be pushed back in (often very painful)
Bleeding from internal hemorrhoids is typically bright red and may appear on toilet paper, drip into the toilet bowl, or streak the stool. Some patients may primarily experience prolapse without significant bleeding. Prolapsing tissue can cause irritation, itching, mucus discharge, and difficulty cleaning after bowel movements.
External Hemorrhoids
Symptomatic external hemorrhoids often appear as bluish, painful lumps outside the anus, usually caused by straining. The overlying skin is firmly attached to underlying tissues, and if a blood clot forms, it can cause severe pain due to increased pressure. Sometimes, the pressure leads to skin breakdown and leakage of clotted blood. Other symptoms include intermittent swelling, pressure, and discomfort from non-thrombosed external hemorrhoids.
Anal Skin Tags: Patients may notice painless, soft tissue around the anus, which are often residual effects of previous external hemorrhoids. These tags can interfere with hygiene after bowel movements or may be considered unsightly. They usually do not require treatment, though surgical removal is sometimes considered.
Causes of Symptomatic Hemorrhoids
Several factors can increase pressure within the abdomen, leading to symptomatic hemorrhoids. These include:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Pregnancy
- Irregular bowel patterns
Over time, these factors can contribute to the prolapse of internal hemorrhoids or thrombosis of external hemorrhoidal tissue.
Treatment of Hemorrhoids
Kshara karma
HAL + RAR
Laser Ablation
Sutured Rectopexy
Hemorrhoids are a common condition that can cause significant discomfort but are often manageable with lifestyle changes and medical treatment. If you experience symptoms of hemorrhoids, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.